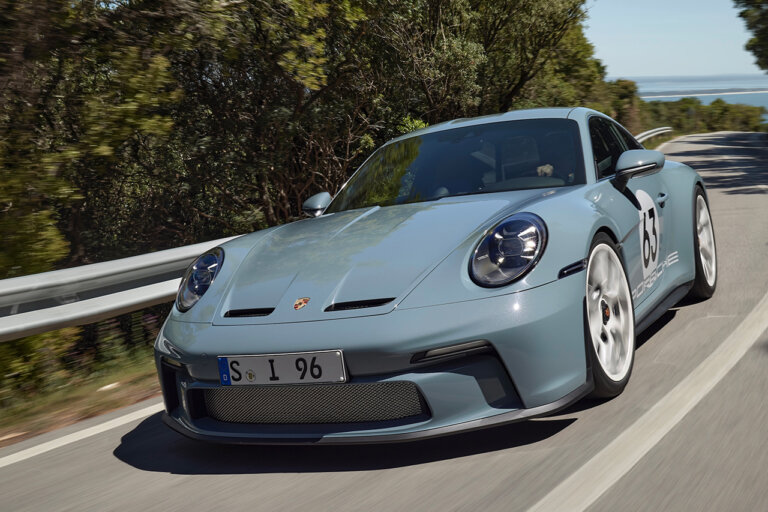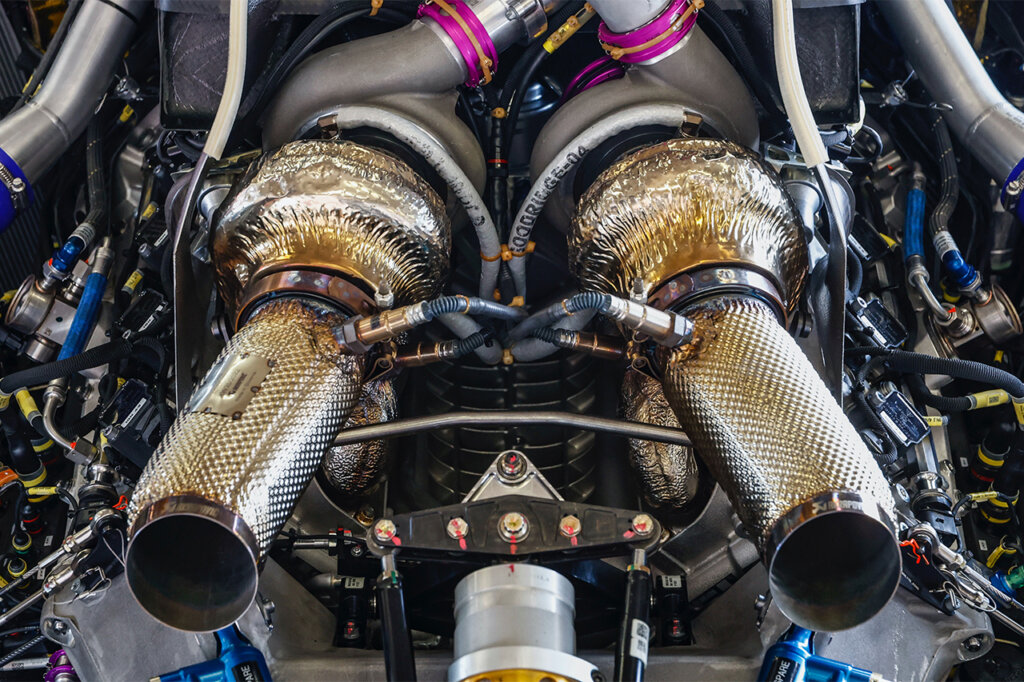
Source: Porsche
Turbocharging has revolutionized engine performance, blending power and efficiency in a way few technologies can rival. From its origins as an industrial innovation to its role in modern high-performance vehicles, the turbocharged engine has carved a unique place in automotive history. By harnessing exhaust gases to deliver a powerful boost, turbocharged engines have become synonymous with enhanced performance and innovation, pushing the boundaries of what internal combustion engines can achieve.
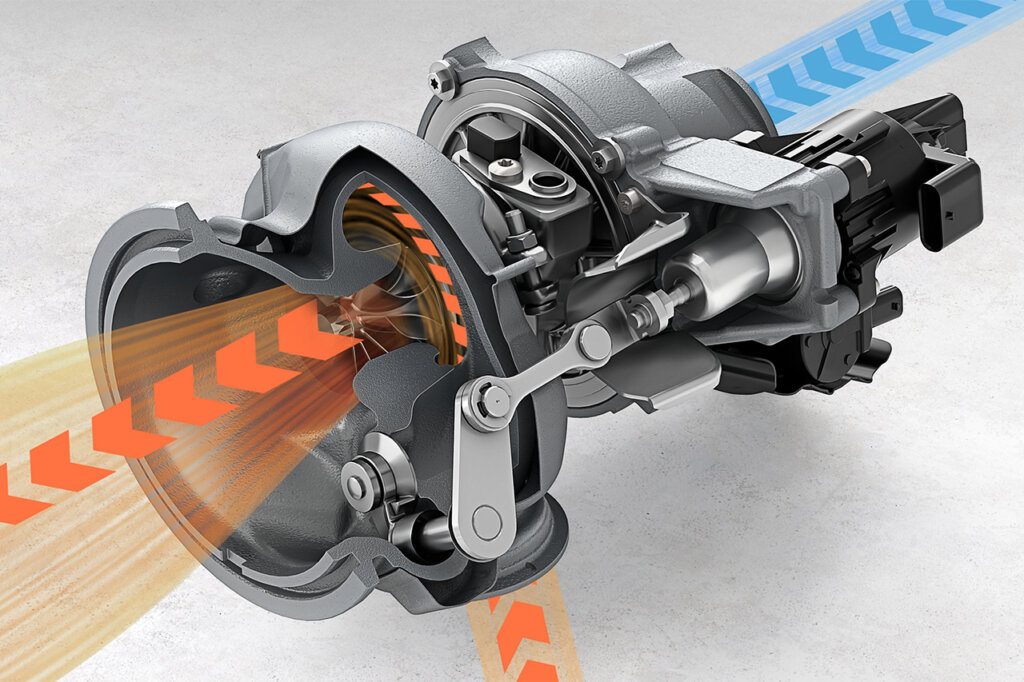
Source: Porsche
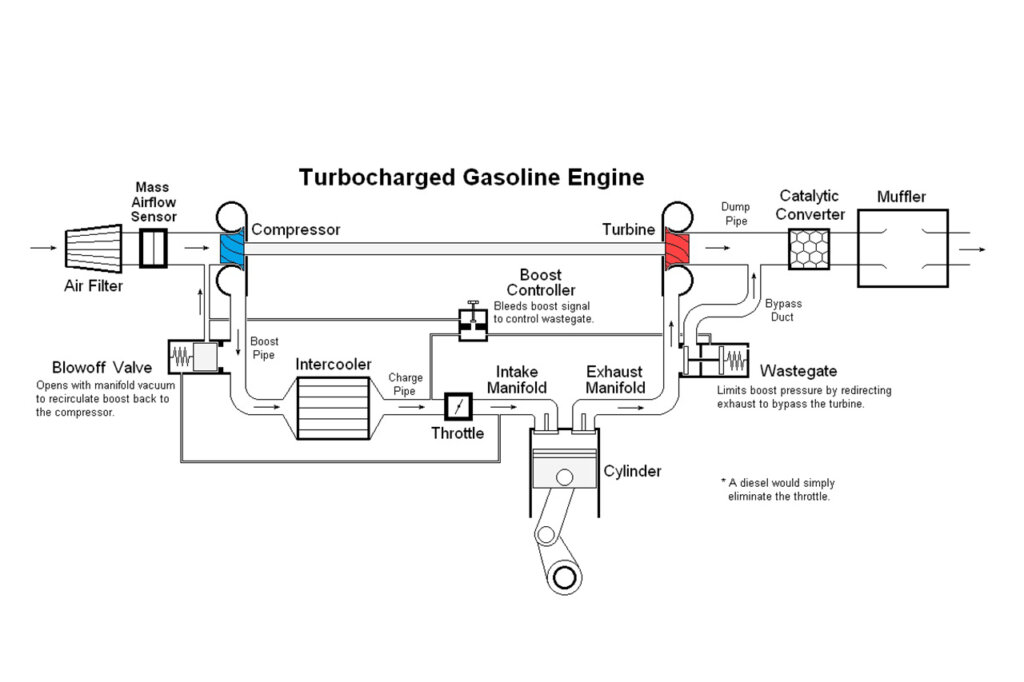
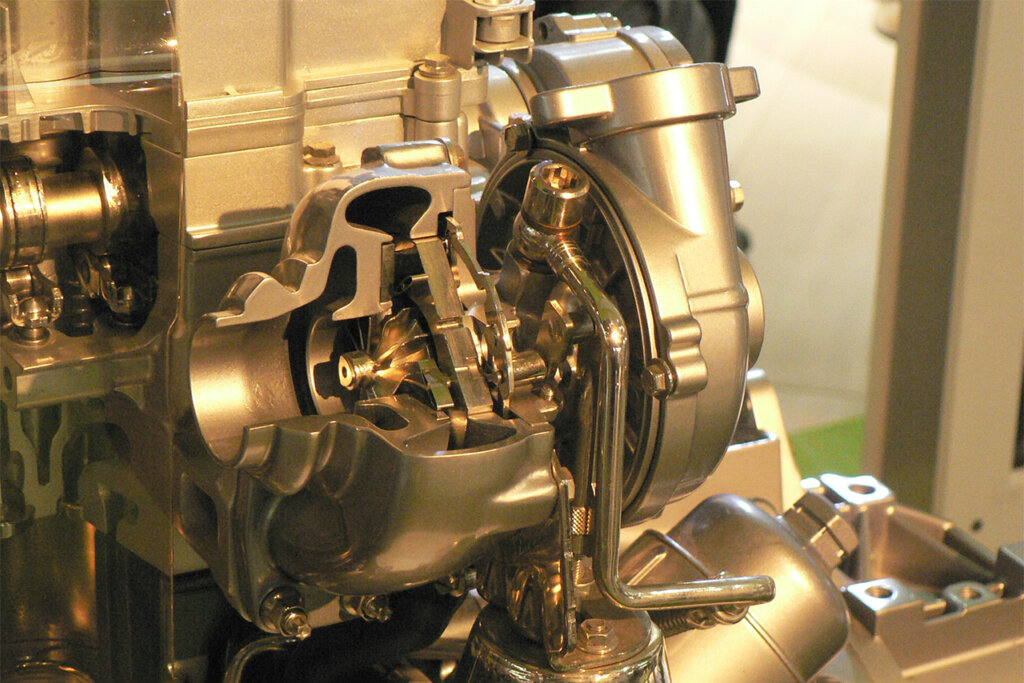
Source: Wiki Commons
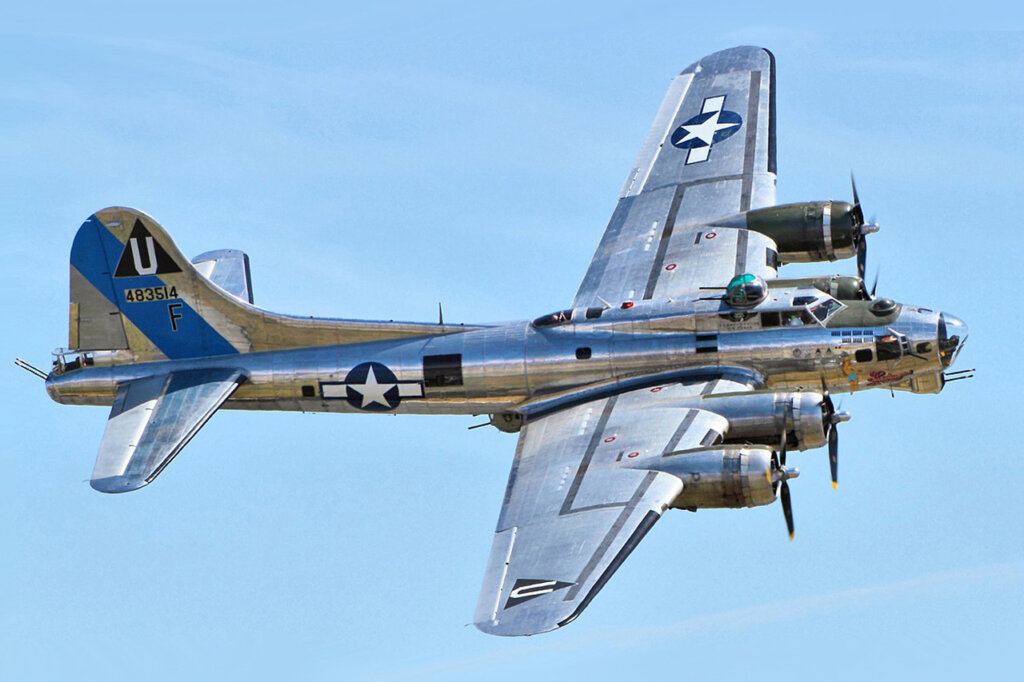
The origins of the turbocharger or turbo or turbo supercharger trace back to 1905 when Swiss engineer Alfred Büchi patented the concept. Büchi aimed to improve the efficiency of diesel engines by using exhaust gases to drive a turbine that compressed incoming air. This increased air density allowed more fuel to be burned, generating greater power without enlarging the engine. Early applications were focused on ships and aircraft, where maximizing power while minimizing weight and space was critical. World War II saw significant advances in turbocharging, with aircraft like the Boeing B-17 Flying Fortress using the technology to maintain engine performance at high altitudes.
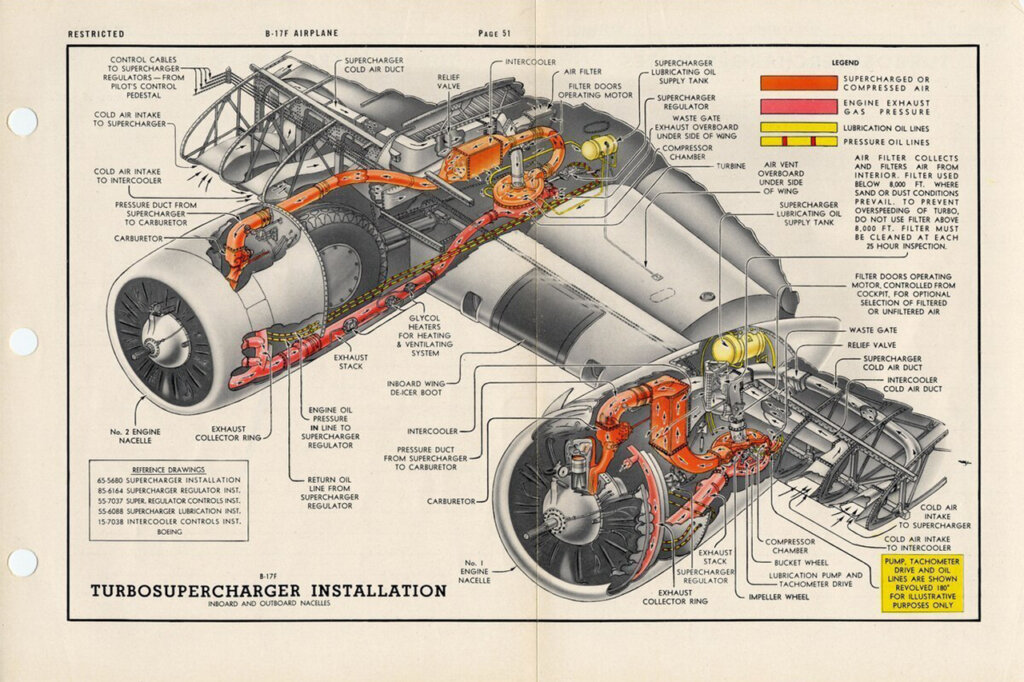
Source: Facebook via PlaneHistoria










