Rotary Power
One of the key distinctions of the Wankel rotary engine lies in its compact size and lightweight construction compared to traditional piston engines. By eliminating many of the moving parts found in piston engines, such as valves, camshafts, and connecting rods, the rotary engine achieves a high power-to-weight ratio and a more favorable power-to-size ratio. This inherent simplicity also translates to fewer vibrations and smoother operation, making it a preferred choice for applications where smoothness and compactness are paramount.
Source: Mazda
Moreover, the Wankel rotary engine offers a unique combination of high-revving capabilities and linear power delivery. Unlike piston engines, which often require gearing to reach high rpm ranges, the rotary engine can achieve remarkably high revs without sacrificing performance or reliability. This characteristic makes it particularly well-suited for sports cars and performance-oriented vehicles, where quick acceleration and responsiveness are highly valued.
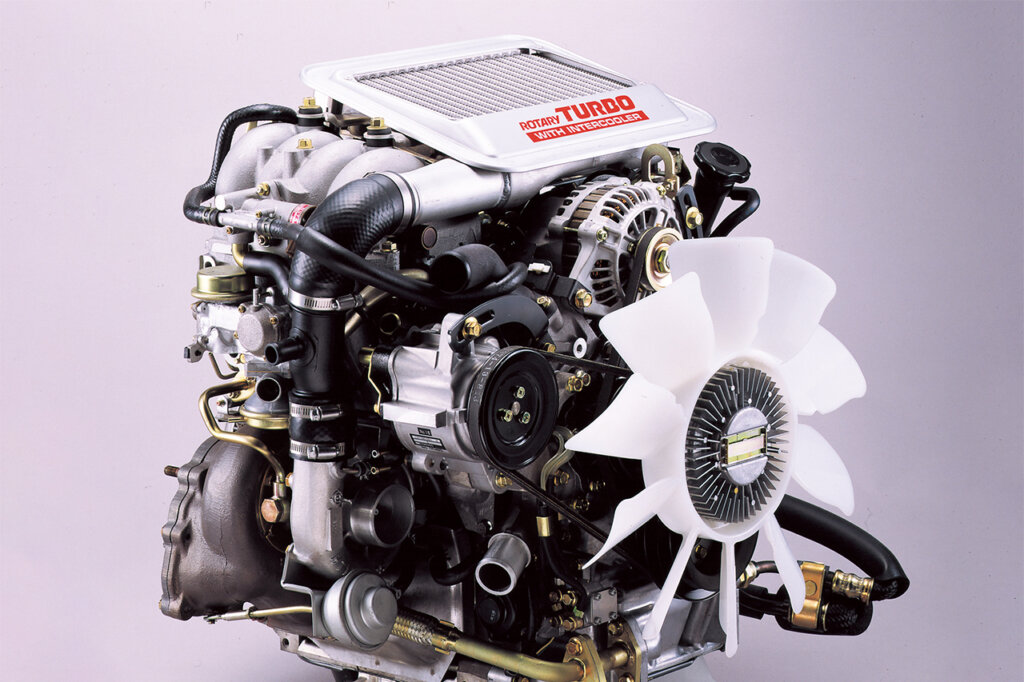

Source: Mazda
Despite its innovative design and inherent advantages, the Wankel rotary engine has faced challenges and criticisms over the years, particularly in terms of fuel efficiency and emissions. Due to its design, rotary engines tend to consume more fuel and produce higher emissions compared to equivalent piston engines. Additionally, issues such as apex seal wear and oil consumption have plagued certain iterations of the rotary engine, leading to reliability concerns among some enthusiasts.









